[ad_1]

Industrial robotics
By Anastasiia Nestrogaeva (Junior Advisor on the Worldwide Initiatives Workforce, Civitta)
Robotics4EU is a Three-years-long EU-funded challenge which advocates for a wider adoption for AI-based robots in four sectors: healthcare, inspection and upkeep of infrastructure, agri-food, and agile manufacturing. Thus, Robotics4EU raises consciousness about non-technological elements in robotics by way of delivering a sequence of workshops to contain the analysis neighborhood, industry representatives and residents.
The workshop “Robots: Mates and Enemies? Social impression of Robotics in Inspection and Upkeep” which came about on the 26th of January, 2022 tackled the issue of interactions between robots and people. Find out how to consider the true impression of robotics on our society? Find out how to resolve if robots are hazardous and should complicate human lives? To what extent does society settle for quickly progressing robotic applied sciences? All these points have been introduced up through the fruitful dialogue on the workshop. Round 30 folks attended the workshop, with 65% of them belonging to the analysis neighborhood and 10% to industry representatives. About 25% comprised most people. The individuals represented 23 totally different international locations, principally European ones.
Find out how to entry reliable AI?
The workshop initiated with the presentation of the challenge and a brainwriting session at higher involvement of individuals into dialogue, then 4 audio system shared their experience with the individuals. The primary speaker was Roberto Zicari who’s an affiliated professor on the Arcada College of Utilized Sciences in Helsinki and an adjunct professor on the Seoul Nationwide College. Additionally, Roberto leads a crew of worldwide specialists who outlined an evaluation course of for Reliable AI, referred to as Z-Inspection®. The speaker enlisted four essential basic ideas which lie down within the EU Framework: respect for human autonomy, prevention of hurt, equity, and explicability. Additionally, there are 7 essential necessities of the EU in the direction of the reliable AI: accountability; societal and environmental well-being; variety, non-discrimination and equity; transparency, privateness and knowledge governance, technical robustness and security.

Regardless of the prevailing necessities, the EU Framework doesn’t take note of the evolving nature of the applied sciences and isn’t contextualised based on numerous area peculiarities. That’s the reason, as Roberto burdened, Z-inspection used a holistic method and created the orchestration course of which helps groups of specialists entry the moral, authorized, technical and area particular implications for using AI services or products. This course of could be employed throughout the entire AI lifecycle and makes use of socio-technical eventualities to determine points. Then, the crew of specialists map to reliable AI (onto the moral classes established by the EU´s Pointers for Reliable AI), execute and resolve (give suggestions to stakeholders).
Embracing our future digital colleagues
Second speech was delivered by Maarit Sandelin who works because the European Community Supervisor in SPRINT Robotics specializing in Robotic Innovation. Maarit defined that SPRINT Robotics is an industry-driven initiative that promotes the event, availability and software of Inspection & Upkeep Robotics all over the world. There are four focuses which embrace security enchancment, value avoidance and discount, environmental efficiency enchancment, and basic efficiency enchancment. Maarit defined that SPRINT Robotics is an industry-driven initiative that promotes the event, availability and software of Inspection & Upkeep Robotics all over the world. There are four focuses which embrace security enchancment, value avoidance and discount, environmental efficiency enchancment, and basic efficiency enchancment.

Maarit burdened that COVID-19 positively has been growing the curiosity of enterprise in robotic options. A complete of 88% of companies worldwide plan on adopting robotic automation into their infrastructure to extend effectivity and security. Additionally, there can be a 12% improve in cargo of robots worldwide and collaborative robots (cobots) will represent 34% of all robotic gross sales by 2025. The speaker observed that many harmful inspection and upkeep actions could be carried out by robots and effectivity is reached primarily by way of the preparation stage. Nevertheless, the principle boundaries for integrating the robotics resolution into operations are rules. In some international locations, the utilization of robotics will not be allowed by the legislature or its interpretations which, in flip, trigger points for service and technical suppliers. Maarit strongly believes that the coverage modifications are wanted to contribute to the adoption of robots.
There are additionally different boundaries of a wide-spread adoption. Firms would want to cut back the workforce, to switch the situation the place an organization operates, and even to switch the entire worth chain. Additionally, the abilities gaps within the native labour markets can be seen as a possible danger which might require correct coaching. Speaking about displacement of jobs, Maarit acknowledged that it’ll proceed and 85 million jobs can be displaced by 2025, however 97 jobs could seem resulting from new division of labor between people and machines. Maarit mentioned there’s a want to point out staff that robotics will not be black-and-one, and reskilling could assist to save lots of a job.
BugWright2 Undertaking
The second half of the workshop featured the BugWright2 Undertaking which does autonomous robotic inspection and upkeep on ship hulls and storage tanks. Alberto Ortiz Rodrigez, who works as a Professor at College of the Balearic Islands, gave the details about the targets and essential actions of the challenge. The challenge has the 5-steps method: multi robotic process allocation; mission planning; autonomous inspection; knowledge put up processing and actionable knowledge era; and upkeep which embrace hull cleansing, augmented actuality, defect marking. Alberto confirmed a number of examples of robots which carry out totally different duties. Lasly, the speaker burdened the significance of the challenge, enlisting four potential impacts. First, it demonstrates how the automated multi-robot applied sciences could be deployed right into a large-scale industrial drawback. Second, such applied sciences result in value effectivity: gasoline saving, decrease service prices, no immobilisation prices. Third, it brings a constructive environmental impression, because it makes the ships and tanks safer, contributes to decrease gasoline consumption and smaller want for antifouling. Lastly, these autonomous inspections are regulated by the World Maritime Organisation (UN).
Human-Robotic-Collaboration: views from work and organisational psychology
The final speech was delivered by Thomas Ellwart who works as a Professor on the College of Trier. He touched the subject of the interactions between robots and people. Whereas citing the principle matter of the workshop “Are robots buddies or enemies?”, the speaker observed that there’s a have to outline a standards of phrases “buddies” and “enemies” or, in different phrases, standards of purposeful / dysfunctional human-robot-interactions (HRC). For psychologists, the principle necessary difficulty to guage among the many HRC is a really particular process of staff on the ship. Thomas is satisfied that there’s a have to mirror summary fashions of robotic options from on-site consumer perspective. Speaking about standards of purposeful HRC, they need to:
Facilitate the correct execution of the duties
Shield well being and improve security
Promote particular person well-being
Develop abilities and human talents
Keep away from below/overload calls for, remoted works, process hindrances, and so on.
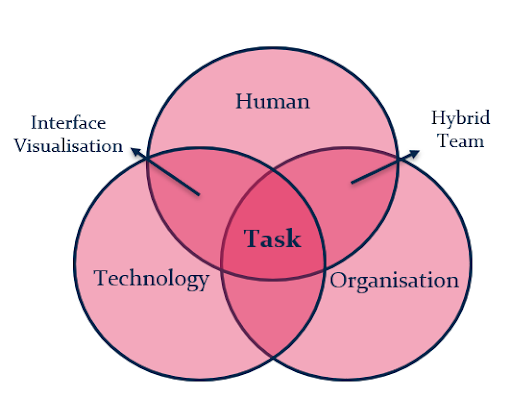 Nevertheless, a excessive robotic autonomy causes some dysfunctional results of excessive robotic autonomy equivalent to exclusion of people for security causes, lowered potentialities to use and prepare abilities, tasks to react in case of failures or disturbances, and low high quality residual duties. This manner, people are excluded from the duty efficiency, however they’re nonetheless in command of system malfunctioning. This manner, a excessive autonomy creates the excessive interdependence between human duties and robots – if a robotic breaks, a process is below hazard, which can postpone the accomplishment of those duties. Additionally, Thomas burdened that acceptance can be a double-faced matter: overtrust is as harmful as distrust.
Nevertheless, a excessive robotic autonomy causes some dysfunctional results of excessive robotic autonomy equivalent to exclusion of people for security causes, lowered potentialities to use and prepare abilities, tasks to react in case of failures or disturbances, and low high quality residual duties. This manner, people are excluded from the duty efficiency, however they’re nonetheless in command of system malfunctioning. This manner, a excessive autonomy creates the excessive interdependence between human duties and robots – if a robotic breaks, a process is below hazard, which can postpone the accomplishment of those duties. Additionally, Thomas burdened that acceptance can be a double-faced matter: overtrust is as harmful as distrust.
To mirror all the standards, the psychologists take a look at particular duties, asking what degree of autonomy the robotic has and what subtasks it performs. Is it making choices or simply monitoring and implementing motion? Thus, from the consumer perspective, there are important components which must be taken under consideration:
Taks (low effectiveness, excessive prices, hindrances)
Know-how (reliability, accuracy, upkeep wants)
Human (e.g. belief, management, cognitive load: what number of robots could be missed by a human)
Organisation (e.g. totally different stakeholders, roles)
As one the goals of Robotics4EU is to develop the Accountable Robotics Evaluation Mannequin, a essential coordinator of the challenge, Anneli Roose, talked about social readiness of robots. Thus, so as to decide this, it is very important work out to what extent a robotic meets a) moral values, b) socio-economic wants, c) knowledge points, d) training and administration points, e) authorized issues. It doesn’t cowl any authorized or regulatory necessities. The muse to construct the Robotics4EU Evaluation Mannequin is the Societal Readiness Ranges, whereas the used instruments are surveys, interviews, debates, workshops, and stakeholder boards involving the robotics analysis neighborhood, coverage makers, and residents.
Panel dialogue
Lastly, the workshop completed with the panel dialogue which introduced up very controversial matters.
Find out how to design a self-assessment mannequin or self-assessment instrument in a approach it could be legitimate in 2-Three years. Is it doable and even related?
Thomas Ellwart burdened that this can be a fairly troublesome query, because it requires to contain the customers and the market. One other matter is whether or not the automated system can be sustainable and adaptable to the altering setting and dependable over the time which is definitely a query to the builders and engineers. Roberto Zicari notices that the Maturity Evaluation Mannequin must be area particular, as a robotic aiding the healthcare could be very totally different from the robotic changing mine employees. Thus, it’s fairly troublesome to switch information obtained within the healthcare sector to the Inspection and Upkeep. He burdened that it could be very fascinating to create an interdisciplinary working group centered on a number of domains and attempt to assess societal readiness degree.
Are the regulatory boundaries vital? Are these boundaries within the EU rules or/and nationwide rules?
Thomas Ellwart states that there are 2 troublesome issues: security and knowledge safety, which come collectively if we’re speaking concerning the regulation on AI. Roberto Zicari talked about that the EU proposed the primary AI Regulation Act, aimed toward regulating any AI-based techniques and options which relies on the chance evaluation method. This proposed act seems to be at AI primarily as a software program, reverse to the classical definition. Nevertheless, which actual composition of hardware and AI poses excessive danger and low danger? Thus, Roberto burdened that there’s a want for discussions amongst researchers, regulation neighborhood and industry specialists. Some individuals additionally observed that the regulatory framework would have to be tailored to the cultural variations all all over the world.
Upcoming Workshop
The upcoming workshop on the 23rd of February 2022, 11-14 CET “Boosting Improvements and Maximising Societal Influence. Function of Digital Innovation Hubs (DIHs) in Robotics for Inspection & Upkeep”. We are going to take a look at digital innovation hubs as a technique to join establishments and SMEs, serving to to shut the information hole of non-technological problems with robotics in Inspection & Upkeep. We are going to deal with alternatives which deliver SMEs and tech startups collectively and the way they’ll doubtlessly increase their improvements within the revered space. The workshop will characteristic representatives from digital innovation hubs, in addition to industry specialists.
tags: c-Industrial-Automation

Robotics4EU
is a Three-year-long challenge funded below the European Union’s Horizon 2020 analysis and innovation programme.

Robotics4EU
is a Three-year-long challenge funded below the European Union’s Horizon 2020 analysis and innovation programme.
[ad_2]
